Electrical substations are the backbone of modern power distribution systems, serving as crucial nodes that facilitate the efficient transfer of electricity from generation sources to end consumers. These substations play a vital role in regulating various parameters of electrical power, ensuring safe and consistent energy flow across diverse applications. This article delves into the different types of substations and their functions, highlighting their significance in the realm of power distribution.
Classification of Substations
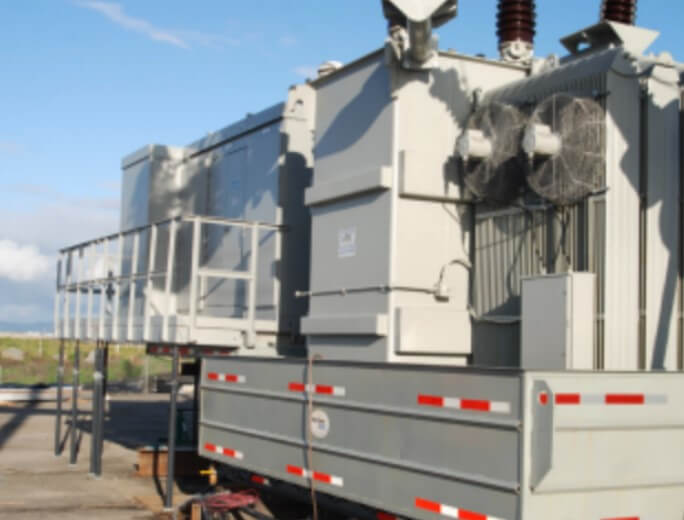
Substations can be broadly classified into several categories based on different criteria, including their application, service, operating voltage levels, and location/design. Each classification reflects a specific role that the substation fulfills within the power distribution network. Becker Mining USA, a prominent player in the field of power distribution solutions, offers a range of reliable and robust substation solutions tailored to demanding environments like mining.

GET IN TOUCH
In a hurry? Call us at 276-285-3841
Substations Based on Application
1. Step-up Substation: Step-up substations are directly linked to power generating stations, as electricity generation often occurs at lower voltage levels. These substations are responsible for stepping up the voltage to enable economical transmission over long distances. Becker Mining's step-up substations stand out for their superior performance and durability, ensuring the efficient transmission of power over extended networks.
2. Step-down Substation: These substations are connected to load centers and serve to transform the transmission voltage to a lower level, typically around 69 kV. They act as sources for distribution substations, which further distribute power to end consumers.
3. Primary Substation: Primary substations are located alongside primary transmission lines and are connected to bulk load centers. They play a pivotal role in stepping down voltage levels for secondary transmission.
4. Secondary Substation: Situated along secondary transmission lines, secondary substations continue the voltage reduction process initiated by primary substations. Their main function is to step down voltage levels for distribution purposes.
5. Distribution Substation: These substations play a crucial role in reducing primary distribution voltages to levels suitable for consumer use. Becker Mining's distribution substations guarantee a stable and reliable power supply for various applications, enhancing the overall reliability of power distribution networks.
6. Mobile Substation: Temporary in nature, mobile substations find utility in large construction projects, offering a short-term power supply to facilitate ongoing operations.
7. Industrial Substation: Also known as bulk substations, industrial substations cater to dedicated consumers such as industries that require substantial power supply. These substations are designed to meet the high power demands of industrial processes.
8. Mining Substation: Mining substations, designed with stringent safety measures, control the electrical power supply from surface to underground mine power stations. Becker Mining specializes in developing mining substations that ensure both safety and efficiency in mining operations, where reliability and safety are paramount.
GET IN TOUCH
In a hurry? Call us at 276-285-3841
Substations Based on Service
1. Converter Substations: These substations are responsible for changing the frequency of the current from higher to lower levels. Additionally, they have the capability to convert between AC and DC, depending on the requirements of the power distribution network.
2. Switching Substations: Switching substations play a crucial role in maintaining grid stability. They facilitate the switching of power lines without altering the voltages and help isolate faulty portions of the system, ensuring uninterrupted power flow.
3. Collector Substations: Often employed in distributed power generation projects, collector substations collect power flow from multiple sources and step up the transmission voltage to distribute the power to the grid efficiently.
Substations Based on Operating Voltage Levels
Another way to categorize substations is based on the voltage levels they operate at. This categorization may vary from one region to another, reflecting the specific requirements and infrastructure of each region's power distribution network. Collaborating with a knowledgeable partner for your electrical engineering needs, like Becker Mining, ensures the selection of an optimal substation configuration that aligns with your operational requirements.
The Role of Substations in Power Distribution
Electrical energy is the lifeblood of modern society, powering homes, industries, transportation, and technology. The journey of electricity from power generation plants to end-users involves a complex web of infrastructure, and substations stand at the heart of this network. These unassuming structures serve as critical nodes that facilitate the transformation, distribution, and regulation of electrical power, ensuring that it reaches its intended destinations safely and efficiently.
Substations act as essential intermediaries between various components of the power system. They are the key points where voltage levels are adjusted, currents are transformed, and the integrity of the grid is maintained. To delve deeper into their significance, let's explore the functions of substations in greater detail.
Voltage Transformation and Regulation
One of the primary functions of substations is voltage transformation. Electricity is generated at power plants in relatively low voltages to minimize energy losses during transmission. However, for efficient long-distance transmission, the voltage needs to be stepped up using transformers. Step-up substations play a pivotal role in this process, elevating the voltage to levels suitable for long-distance transmission, thus reducing energy losses.
Conversely, as electricity approaches its destination, step-down substations further reduce the voltage to levels appropriate for distribution to homes and businesses. This voltage transformation is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and stability of the entire power system.
Grid Stability and Fault Isolation
The stability of the electrical grid is paramount to ensuring uninterrupted power supply. Switching substations play a crucial role in this aspect. These substations allow power lines to be switched without altering voltage levels, enabling efficient maintenance, fault isolation, and load balancing. In the event of a fault or disruption in one part of the system, switching substations can isolate the faulty section, preventing widespread outages and ensuring the rest of the network continues to function smoothly.
Adapting to Distributed Generation
The landscape of power generation is evolving rapidly with the integration of renewable energy sources and distributed generation systems. This transition presents unique challenges in terms of power flow management and synchronization with the grid. Collector substations are specially designed to aggregate power generated from multiple distributed sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines. These substations step up the voltage to ensure efficient integration of the generated power into the grid, contributing to a more sustainable and decentralized power generation ecosystem.
Safety and Specialized Applications
Substations are not one-size-fits-all structures; their design and features are tailored to their intended applications. For instance, mining substations, as provided by Becker Mining, incorporate heightened safety measures due to the hazardous environment of mining operations. These substations are engineered to withstand challenging conditions, ensuring reliable power supply while minimizing risks to personnel and equipment.
Future of Substations
As the energy landscape continues to evolve, substations are poised to undergo further advancements to accommodate emerging technologies. The integration of smart grid components, such as sensors and automation, will enhance the monitoring and control of substations, leading to quicker fault detection and response times. Additionally, as renewable energy sources become more prevalent, substations will play a pivotal role in managing the intermittent nature of these sources, ensuring grid stability and reliable power supply.

GET IN TOUCH
In a hurry? Call us at 276-285-3841
Conclusion
In the intricate tapestry of power distribution systems, substations play a pivotal role in ensuring the seamless flow of electricity from generation to consumption. The design and functionality of these substations are influenced by a myriad of factors, including their application, service, operating voltage levels, and location or design. Becker Mining USA stands as a reliable provider of advanced substation solutions, ensuring efficient power distribution even in the most demanding and challenging environments. Whether it's stepping up or stepping down voltages, converting currents, or collecting power flow, substations remain the unsung heroes of the modern power distribution landscape.
Make an Informed Decision
To maximize energy efficiency and cost savings, businesses must evaluate their specific needs and applications when selecting a substations. For expert guidance in choosing the best mining substations for your requirements, reach out to Becker Mining USA today.
Products We Offer:
- Explosion Proof Equipment
- Transformers
- Arc Guard
- Longwall Electrical Systems
- Capacitor Trip Devices
- Electrical Equipments like capacitor banks, switch houses, junctions, and splice boxes.
Since 1971, Becker/SMC has been a trailblazer in delivering top-notch electrical components, open-type and explosion-proof motor starters, longwall electrical controls, and power distribution equipment. Our unwavering commitment to quality and customer satisfaction has made us a trusted name in the industry. Contact us today!